Investigation of Co-incorporated pristine and Fe-doped Li3V2(PO4)3 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
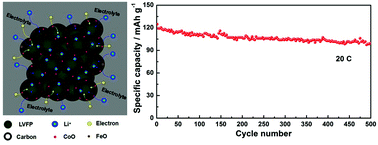
Monoclinic Li3V2(PO4)3/C (LVP/C) and Li3V1.95Fe0.05(PO4)3/C (LVFP/C) composites were successfully modified by cobalt incorporation. The effects of cobalt incorporation on the structure, morphology and electrochemical performance of the LVP/C and LVFP/C composites were systematically investigated. The results show that most Co exists in the form of CoO and forms a hybrid layer with the carbon coating on the surface of the LVP and LVFP particles; moreover, a small part of Co enters into the LVP or LVFP lattices due to atomic diffusion. Compared with LVP/C and LVFP/C, Co-incorporated samples exhibit better electrochemical performance. In particular, under the common effect of doping and a hybrid layer (carbon and metal oxides) coating, the LVFP/C-Co electrode displays a prominent initial capacity of 124.7 mA h g−1 and a very low capacity fading of ∼0.04% per cycle even after 500 cycles at 20 C. This novel co-modification method with cation doping and a hybrid layer (carbon and metal oxide) coating is a highly effective way to improve the electrochemical performance and has great potential to be easily used to modify other cathode materials with poor electrical conductivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...