DNA binding of Pd(TC3), a conformable cationic porphyrin with a long-lived triplet state†
Abstract
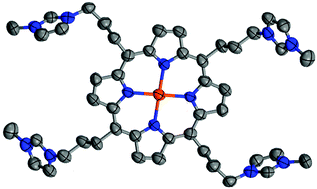
The goal of this work has been to synthesize and investigate Pd(TC3), an intercalating porphyrin that has conformable substituents capable of groove binding to B-form DNA. (TC3 denotes the doubly deprotonated form of 5,10,15,20-tetra[3-(3′-methylimidazolium-1′-yl)prop-1-yl]porphyrin.) Palladium(II) is an apt choice for the central metal ion because it remains strictly four-coordinate and provides for a luminescent triplet excited state with a long lifetime. The DNA hosts are hairpin-forming sequences programmed to differ in base composition. Luminescence, absorbance, and circular dichroism results are consistent with the idea that congruent structural reorganization takes place at the host and ligand during uptake. Photoexcitation of DNA-bound Pd(TC3) generates a comparatively modest steady state concentration of singlet oxygen, due to a relatively slow reaction with molecular oxygen in solution. The sheer size of the substituent groups disfavors quenching, but groove-binding interactions compound the problem by inhibiting mobility. The results show how ligand design affects adduct structure as well as function.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...