Nonaqueous electrocatalytic water oxidation by a surface-bound Ru(bda)(L)2 complex†
Abstract
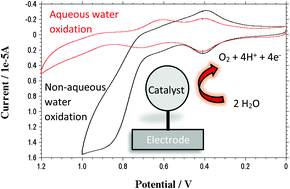
The rate of electrocatalytic water oxidation by the heterogeneous water oxidation catalyst [Ru(bda)(4-O(CH2)3P(O3H2)2-pyr)2], 1, (pyr = pyridine; bda = 2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-dicarboxylate) on metal oxide surfaces is greatly enhanced relative to water as the solvent. In these experiments with propylene carbonate (PC) as the nonaqueous solvent, water is the limiting reagent. Mechanistic studies point to atom proton transfer (APT) as the rate limiting step in water oxidation catalysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...