An efficient and sensitive fluorescent pH sensor based on amino functional metal–organic frameworks in aqueous environment†
Abstract
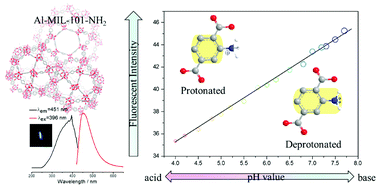
A pH sensor is fabricated via a reaction between an AlIII salt and 2-aminoterephthalic acid in DMF which leads to a MOF (Al-MIL-101-NH2) with free amino groups. The Al-MIL-101-NH2 samples show good luminescence and an intact structure in aqueous solutions with pH ranging from 4.0 to 7.7. Given its exceptional stability and pH-dependent fluorescence intensity, Al-MIL-101-NH2 has been applied to fluorescent pH sensing. Significantly, in the whole experimental pH range (4.0–7.7), the fluorescence intensity almost increases with increasing pH (R2 = 0.99688) which can be rationalized using a linear equation: I = 2.33 pH + 26.04. In addition, error analysis and cycling experiments have demonstrated the accuracy and utilizability of the sensor. In practical applications (PBS and lake water), Al-MIL-101-NH2 also manifests its analytical efficiency in pH sensing. And the samples can be easily isolated from an aqueous solution by incorporating Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Moreover, the possible sensing mechanism based on amino protonation is discussed in detail. This work is on of the few cases for integrated pH sensing systems in aqueous solution based on luminescent MOFs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...