Luminescent and magnetic materials with a high content of Eu3+-EDTA complexes†
Abstract
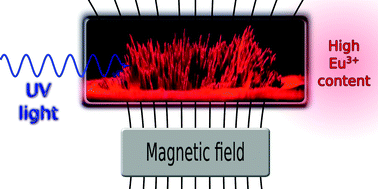
Bifunctional optical magnetic materials with a high europium content have been prepared. Chelating groups were introduced on the Fe3O4 surface with organosilanes containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) derivatives, which were previously prepared via a reaction between EDTA-dianhydride and aminoalkoxysilane agents: 3-(trimethoxysilyl)propylamine (1N), N-[3(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]ethylenediamine (2N) and N1-(3-trimethoxysilylpropyl)diethylenetriamine) (3N). The first coordination sphere of Ln-EDTA complexes present on the modified surfaces of Fe3O4 particles was completed by addition of β-diketonate ligands (tta: thenoyltrifluoroacetone, dbm: dibenzoylmethane, bzac: benzoylacetone and acac: acetylacetone) in order to improve their luminescence properties. The materials were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence (WDXRF) and Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy as well as by zeta potential measurements and luminescence spectroscopy. The hybrid materials exhibited intense red emission, which can be assigned to the 4f–4f transitions of the Eu3+ ion, indicating an efficient intramolecular ligand-to-metal energy transfer. The experimental intensity parameters (Ω2 and Ω4), lifetimes (τ), as well as radiative (Arad) and non-radiative (Anrad) decay rates of the Eu3+ ion were determined and discussed. The strategies used to obtain these materials may contribute to the development of several bifunctional systems for practical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...