Synthesis, structure, and physical properties of new rare earth ferrocenoylacetonates†
Abstract
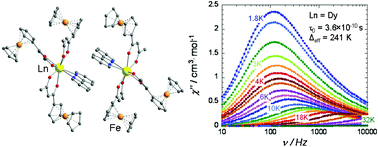
New ferrocenoylacetonate complexes of several rare earth elements, [Ln(fca)3(bpy)]·MeC6H5 (Ln = Pr (1), Eu (2), Gd (3), Tb (4), Dy (5), Ho (6), Y (7); bpy – 2,2′-bipyridine; Hfca – FcCOCH2COMe) as well as scandium ferrocenoylacetonate [Sc(fca)3]·0.5MeC6H5 (8), were synthesized and characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. In the crystal lattice of the isostructural complexes 1–7, two [Ln(fca)3(bpy)] molecules form a pair due to stacking interactions between the bpy ligands. The Ln3+ ions are coordinated in a square antiprism geometry with a coordination number of 8. The Sc3+ ions in complex 8 are coordinated in an octahedral geometry. Thermolysis of complexes 1–7 was studied under air and argon atmospheres; in the first case, it affords perovskites LnFeO3 as one of the products. Complexes 4–6 display single-molecule magnet properties, and the effective relaxation barrier for the Dy complex 5, was found to be Δeff/kB = 241 K, which is one of the highest values obtained for a mononuclear β-diketonate lanthanide complex.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...