Synthesis and structural characterization of monomeric mercury(ii) selenolate complexes derived from 2-phenylbenzamide ligands†
Abstract
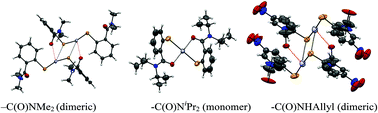
Monomeric Hg(II) selenolate complexes derived from 2-phenylbenzamide ligands were prepared by oxidative addition of diselenides [{C6H4(CONR2)Se}2, R = Me, Et, iPr] to elemental Hg and reductive cleavage of the Se–N bond of isoselenazolone derivatives [(NO2)C6H3(CONSe)R, (R = allyl, nbutyl)] followed by the treatment with HgCl2. The complexes have been characterized by multinuclear NMR (1H, 13C and 77Se) spectroscopy and mass spectrometry which suggest the monomeric form of these in solution. The molecular structures of diselenides [C6H4(CONR2)Se]2 and mercury selenolates [Hg{(NO2)C6H3(CONH-C3H5)Se}2], [Hg{C6H4(CONiPr2)Se}2] and [Hg{C6H4(CONMe2)Se}2] were established by a single crystal X-ray diffraction study. Diselenides show strong intramolecular non-bonded Se⋯O interactions, which are influenced by the nature of C(O)N![[R with combining low line]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0052_0332.gif) 2 and decrease with the sterically bulky alkyl substituent (Se⋯O = 2.823 Å for R = di-Me, 2.760 Å for R = allyl, and 3.157 Å for R = di-iPr). Mercury complexes derived from less bulky 2-phenyl-N,N-dialkylbenzamide ligands associated with poor or no intramolecular non-bonded Hg⋯O interactions (4.91 Å for R = di-Me, 4.199 Å for R = allyl) and instead strong intermolecular Hg⋯O [2.792(3) and 2.820(4) Å] for di-Me and allyl and Hg⋯Se [3.3212(5) and 3.4076(8) Å] interactions were observed which lead to a dimeric form in the crystals. On the other hand, the mercury complex derived from the sterically bulky diisopropyl amide ligand shows a strong intramolecular non-bonded Hg⋯O (2.860 Å) interaction, adopts linear geometry and exists as a monomer. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of the mercury selenolate complexes revealed two-step decomposition which leads to the formation of HgSe. The mercury selenolate complex 3c derived from the sterically bulky 2-phenyl-N,N-diisopropylbenzamide ligand decomposed to give HgSe in the range of 220–300 °C.
2 and decrease with the sterically bulky alkyl substituent (Se⋯O = 2.823 Å for R = di-Me, 2.760 Å for R = allyl, and 3.157 Å for R = di-iPr). Mercury complexes derived from less bulky 2-phenyl-N,N-dialkylbenzamide ligands associated with poor or no intramolecular non-bonded Hg⋯O interactions (4.91 Å for R = di-Me, 4.199 Å for R = allyl) and instead strong intermolecular Hg⋯O [2.792(3) and 2.820(4) Å] for di-Me and allyl and Hg⋯Se [3.3212(5) and 3.4076(8) Å] interactions were observed which lead to a dimeric form in the crystals. On the other hand, the mercury complex derived from the sterically bulky diisopropyl amide ligand shows a strong intramolecular non-bonded Hg⋯O (2.860 Å) interaction, adopts linear geometry and exists as a monomer. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of the mercury selenolate complexes revealed two-step decomposition which leads to the formation of HgSe. The mercury selenolate complex 3c derived from the sterically bulky 2-phenyl-N,N-diisopropylbenzamide ligand decomposed to give HgSe in the range of 220–300 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...