A trinuclear ruthenium complex as a highly efficient molecular catalyst for water oxidation†
Abstract
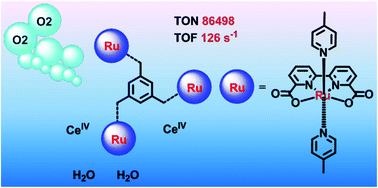
A trinuclear ruthenium complex, 3, was designed and synthesized with the ligand 2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-dicarboxylic acid (bda) and we found that this complex could function as a highly efficient molecular catalyst for water oxidation in homogeneous systems. This trinuclear molecular water oxidation catalyst, 3, displayed much higher efficiencies in terms of turnover numbers and initial oxygen evolution rate than its counterparts, a binuclear catalyst, 2, and a mononuclear catalyst, 1, in both chemically driven and photochemically driven water oxidation based on either the whole catalytic molecules or just the active Ru centers. The reasons for the superior performance of catalyst 3 were discussed and we believe that multiple Ru centers in a single molecule are indeed beneficial for increasing the probability of the formation of O–O bonds through an intramolecular radical coupling pathway.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...