A ternary Cu2O–Cu–CuO nanocomposite: a catalyst with intriguing activity†
Abstract
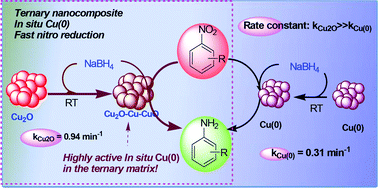
In this work, the syntheses of Cu2O as well as Cu(0) nanoparticle catalysts are presented. Copper acetate monohydrate produced two distinctly different catalyst particles with varying concentrations of hydrazine hydrate at room temperature without using any surfactant or support. Then both of them were employed separately for 4-nitrophenol reduction in aqueous solution in the presence of sodium borohydride at room temperature. To our surprise, it was noticed that the catalytic activity of Cu2O was much higher than that of the metal Cu(0) nanoparticles. We have confirmed the reason for the exceptionally high catalytic activity of cuprous oxide nanoparticles over other noble metal nanoparticles for 4-nitrophenol reduction. A plausible mechanism has been reported. The unusual activity of Cu2O nanoparticles in the reduction reaction has been observed because of the in situ generated ternary nanocomposite, Cu2O–Cu–CuO, which rapidly relays electrons and acts as a better catalyst. In this ternary composite, highly active in situ generated Cu(0) is proved to be responsible for the hydride transfer reaction. The mechanism of 4-nitrophenol reduction has been established from supporting TEM studies. To further support our proposition, we have prepared a compositionally similar Cu2O–Cu–CuO nanocomposite using Cu2O and sodium borohydride which however displayed lower rate of reduction than that of the in situ produced ternary nanocomposite. The evolution of isolated Cu(0) nanoparticles for 4-nitrophenol reduction from Cu2O under surfactant-free condition has also been taken into consideration. The synthetic procedures of cuprous oxide as well as its catalytic activity in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol are very convenient, fast, cost-effective, and easily operable in aqueous medium and were followed spectrophotometrically. Additionally, the Cu2O-catalyzed 4-nitrophenol reduction methodology was extended further to the reduction of electronically diverse nitroarenes. This concise catalytic process in aqueous medium at room temperature revealed an unprecedented catalytic performance which would draw attention across the whole research community.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...