Non-directed aromatic C–H amination: catalytic and mechanistic studies enabled by Pd catalyst and reagent design†
Abstract
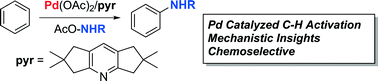
This manuscript describes the systematic development of pyridine-type ligands, which promote the Pd catalyzed, non-directed amination of benzene in combination with novel, hydroxylamine-based electrophilic amination reagents. DFT calculations and mechanistic experiments provide insights into the factors influencing the arene C–H amination protocol.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...