Flame-pyrolysis-prepared catalysts for the steam reforming of ethanol
Abstract
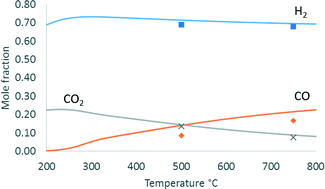
An innovative flame pyrolysis method was employed for the preparation of Ni-based catalysts for the steam reforming of ethanol. Titania and lanthana supports, characterised by variable acidity and Ni loading, were compared as well as the different procedures to add the Ni active phase to the support, thus affecting the metal dispersion. Samples characterisation provided evidence that the one-pot preparation of the catalyst by flame pyrolysis (FP) resulted in the formation of a mixed oxide phase and, thus, in a higher Ni dispersion, even at the highest loading. The metal–support interaction was also strengthened when preparing the samples by FP rather than by conventional impregnation. Steam reforming at 750 °C resulted in full ethanol conversion without by-products, such that a fuel processor able to feed a 5 kWe + 5 kWt fuel cell may operate with ca. 1.35 kg of catalyst. Tests at lower temperature were also carried out, focusing on the optimization of the resistance to coking. The best results at 500 °C were achieved for the FP-prepared sample supported over La2O3 and containing 15 wt% Ni as the active phase.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...