Strontium promoted activated carbon-supported gold catalysts for non-mercury catalytic acetylene hydrochlorination†
Abstract
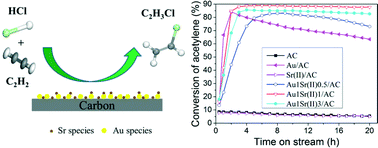
Bimetallic gold–strontium catalysts were prepared and assessed for the effect of a Sr(II) additive on the catalytic performance of gold-based catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination, combined with characterization using N2 adsorption/desorption, thermogravimetric analysis, temperature-programmed reduction/desorption, powder X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, atomic absorption spectrophotometry and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The optimal catalytic performance is obtained over an Au1Sr(II)1/AC catalyst with acetylene conversion of 87.7% and selectivity for VCM of 99.8%, after 20 h on stream under the conditions of a temperature of 180 °C, a C2H2 gas hourly space velocity (GHSV) of 762 h−1, and a feed volume ratio HCl/C2H2 of 1.15, which is an increase of 24.3% compared with acetylene conversion of 63.4% after 20 h on stream under the same conditions over a monometallic Au/AC catalyst. It is indicated that the addition of Sr(II) can disperse the Au species well and inhibit carbon deposition on the catalyst surface; the Sr(II) additive can enhance the adsorption of the two reactants, acetylene and hydrogen chloride, on the catalyst and inhibit the reduction of Au3+ to Au0 during the preparation and reaction, consequently enhancing the catalytic activity and long-term stability of gold-based catalysts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...