Nature of intramolecular interactions of vitamin C in view of interacting quantum atoms: the role of hydrogen bond cooperativity on geometry†
Abstract
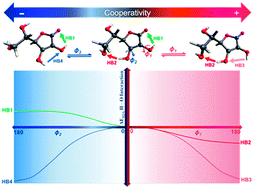
The conformational analysis of six dihedral angles was calculated by second-order Moller–Plesset perturbation theory (MP2) with the correlation-consistent aug-cc-pVDZ basis set. The quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM) was applied to gain a description of the atoms and chemical bonds. A high content of hydroxyl groups in vitamin C's (VC) structure leads to a wide range of intramolecular interactions. The nature of these interactions within the selected VC conformers was studied in view of the interacting quantum atom (IQA) approach. Complete IQA analysis of the atomic and interatomic interaction energies indicated hydrogen bond formation was responsible for the stability of most of the local minima in the potential energy surface. In these conformers, the tandem participation of interactions was operating by way of two- or three-centered (bifurcated) cooperative networks. For the intramolecular hydrogen bond interplay in cooperativity, changes of the IQA atomic and interatomic interaction energies of the participant interactions were monitored during the formation of cooperative networks. The results of the intramolecular cooperativity were evaluated with changes of the delocalization index and bond distances.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...