Chain length, temperature and solvent effects on the structural properties of α-aminoisobutyric acid homooligopeptides†
Abstract
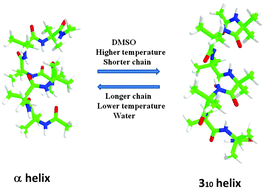
Non-coded α-amino acids, originally exploited by nature, have been successfully reproduced by recent synthetic strategies to confer special structural and functional properties to small peptides. The most known and well-studied atypical residue is α-aminoisobutyric acid (Aib), which is contained in a fairly large number of peptides with known antibiotic effects. Here, we report on a molecular dynamics (MD) study of a series of homooligopeptides based on α-aminoisobutyric acid (Aib) with increasing length (Ac-(Aib)n-NMe, n = 5, 6, 7 and 10) and at various temperatures, employing a recent extension of the AMBER force field tailored for the Aib residue. Solvent effects have been analyzed by comparative MD simulations of a heptapeptide in water and dimethylsulfoxide at different temperatures. Our results show that the preference for the 310- and/or α-helix structures, which typically characterize Aib based peptides, is finely tuned by several factors including the chain length, temperature and solvent nature. While the transitions between intra-molecular i → i + 3 and i → i + 4 hydrogen bonds characterizing 310 and α-helices, respectively, are rather fast in small peptides (in the picosecond timescale), our analysis shows that the above physical and chemical factors modulate the relative equilibrium populations of the two helical structures. The obtained results nicely agree with available experimental data and support the use of the new force field for modeling Aib containing peptides.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...