A broken-symmetry density functional study of structures, energies, and protonation states along the catalytic O–O bond cleavage pathway in ba3 cytochrome c oxidase from Thermus thermophilus†
Abstract
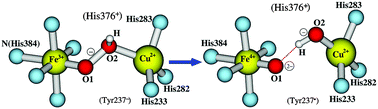
Broken-symmetry density functional calculations have been performed on the [Fea3, CuB] dinuclear center (DNC) of ba3 cytochrome c oxidase from Thermus thermophilus in the states of [Fea33+–(HO2)−–CuB2+, Tyr237−] and [Fea34+![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O2−, OH−–CuB2+, Tyr237˙], using both PW91-D3 and OLYP-D3 functionals. Tyr237 is a special tyrosine cross-linked to His233, a ligand of CuB. The calculations have shown that the DNC in these states strongly favors the protonation of His376, which is above propionate-A, but not of the carboxylate group of propionate-A. The energies of the structures obtained by constrained geometry optimizations along the O–O bond cleavage pathway between [Fea33+–(O–OH)−–CuB2+, Tyr237−] and [Fea34+
O2−, OH−–CuB2+, Tyr237˙], using both PW91-D3 and OLYP-D3 functionals. Tyr237 is a special tyrosine cross-linked to His233, a ligand of CuB. The calculations have shown that the DNC in these states strongly favors the protonation of His376, which is above propionate-A, but not of the carboxylate group of propionate-A. The energies of the structures obtained by constrained geometry optimizations along the O–O bond cleavage pathway between [Fea33+–(O–OH)−–CuB2+, Tyr237−] and [Fea34+![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O2−⋯HO−–CuB2+, Tyr237˙] have also been calculated. The transition of [Fea33+–(O–OH)−–CuB2+, Tyr237−] → [Fea34+
O2−⋯HO−–CuB2+, Tyr237˙] have also been calculated. The transition of [Fea33+–(O–OH)−–CuB2+, Tyr237−] → [Fea34+![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O2−⋯HO−–CuB2+, Tyr237˙] shows a very small barrier, which is less than 3.0/2.0 kcal mol−1 in PW91-D3/OLYP-D3 calculations. The protonation state of His376 does not affect this O–O cleavage barrier. The rate limiting step of the transition from state A (in which O2 binds to Fea32+) to state PM ([Fea34+
O2−⋯HO−–CuB2+, Tyr237˙] shows a very small barrier, which is less than 3.0/2.0 kcal mol−1 in PW91-D3/OLYP-D3 calculations. The protonation state of His376 does not affect this O–O cleavage barrier. The rate limiting step of the transition from state A (in which O2 binds to Fea32+) to state PM ([Fea34+![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O2−, OH−–CuB2+, Tyr237˙], where the O–O bond is cleaved) in the catalytic cycle is, therefore, the proton transfer originating from Tyr237 to O–O to form the hydroperoxo [Fea33+–(O–OH)−–CuB2+, Tyr237−] state. The importance of His376 in proton uptake and the function of propionate-A/neutral-Asp372 as a gate to prevent the proton from back-flowing to the DNC are also shown.
O2−, OH−–CuB2+, Tyr237˙], where the O–O bond is cleaved) in the catalytic cycle is, therefore, the proton transfer originating from Tyr237 to O–O to form the hydroperoxo [Fea33+–(O–OH)−–CuB2+, Tyr237−] state. The importance of His376 in proton uptake and the function of propionate-A/neutral-Asp372 as a gate to prevent the proton from back-flowing to the DNC are also shown.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Developments in Density Functional Theory

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...