Structural variety beyond appearance: high-pressure phases of CrB4 in comparison with FeB4†
Abstract
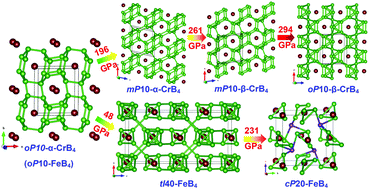
Employing particle swarm optimization (PSO) combined with first-principles calculations, we systemically studied high-pressure behaviors of hard CrB4. Our predictions reveal a distinct structural evolution under pressure for CrB4 despite having the same initial structure as FeB4. CrB4 is found to adopt a new P2/m structure above 196 GPa, another Pm structure at a pressure range of 261–294 GPa and then a Pmma structure beyond 294 GPa. Instead of puckering boron sheets in the initial structure, the high-pressure phases have planar boron sheets with different motifs upon compression. Comparatively, FeB4 prefers an I41/acd structure over 48 GPa with tetrahedron B4 units and a P213 structure above 231 GPa having equilateral triangle B3 units. Significantly, CrB4 exhibits persistent metallic behavior in contrast with the semiconducting features of FeB4 upon compression. The varied pressure response of hard tetraborides studied here is of importance for understanding boron-rich compounds and designing new materials with superlative properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...