Extremely strong bipolar optical interactions in paired graphene nanoribbons†
Abstract
Graphene is an excellent multi-functional platform for electrons, photons, and phonons due to exceptional electronic, photonic, and thermal properties. When combining its extraordinary mechanical characteristics with optical properties, graphene-based nanostructures can serve as an appealing platform for optomechanical applications at the nanoscale. Here, we demonstrate, using full-wave simulations, the emergence of extremely strong bipolar optical forces, or, optical binding and anti-binding, between a pair of coupled graphene nanoribbons, due to the remarkable confinement and enhancement of optical fields arising from the large effective mode indices. In particular, the binding and anti-binding forces, which are about two orders of magnitude stronger than that in metamaterials and high-Q resonators, can be tailored by selective excitation of either the even or the odd optical modes, achievable by tuning the relative phase of the lightwaves propagating along the two ribbons. Based on the coupled mode theory, we derive analytical formulae for the bipolar optical forces, which agree well with the numerical results. The attractive optical binding force Fby and the repulsive anti-binding force Fay exhibit a remarkably different dependence on the gap distance g between the nanoribbons and the Fermi energy EF, in the forms of 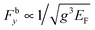 and Fay ∝ 1/E2F. With EF dynamically tunable by bias voltage, the bipolar forces may provide a flexible handle for active control of the nanoscale optomechanical effects, and also, might be significant for optoelectronic and optothermal applications as well.
and Fay ∝ 1/E2F. With EF dynamically tunable by bias voltage, the bipolar forces may provide a flexible handle for active control of the nanoscale optomechanical effects, and also, might be significant for optoelectronic and optothermal applications as well.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...