Protein structural robustness to mutations: an in silico investigation†
Abstract
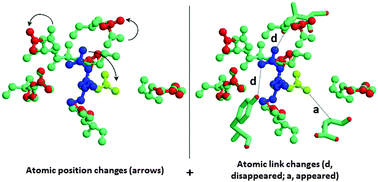
Proteins possess qualities of robustness and adaptability to perturbations such as mutations, but occasionally fail to withstand them, resulting in loss of function. Herein, the structural impact of mutations is investigated independently of the functional impact. Primarily, we aim at understanding the mechanisms of structural robustness pre-requisite for functional integrity. The structural changes due to mutations propagate from the site of mutation to residues much more distant than typical scales of chemical interactions, following a cascade mechanism. This can trigger dramatic changes or subtle ones, consistent with a loss of function and disease or the emergence of new functions. Robustness is enhanced by changes producing alternative structures, in good agreement with the view that proteins are dynamic objects fulfilling their functions from a set of conformations. This result, robust alternative structures, is also coherent with epistasis or rescue mutations, or more generally, with non-additive mutational effects and compensatory mutations. To achieve this study, we developed the first algorithm, referred to as Amino Acid Rank (AAR), which follows the structural changes associated with mutations from the site of the mutation to the entire protein structure and quantifies the changes so that mutations can be ranked accordingly. Assessing the paths of changes opens the possibility of assuming secondary mutations for compensatory mechanisms.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...