Mechanisms and energetics for N-glycosidic bond cleavage of protonated 2′-deoxyguanosine and guanosine†
Abstract
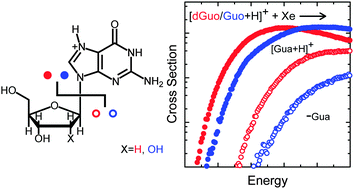
Experimental and theoretical investigations suggest that hydrolysis of N-glycosidic bonds generally involves a concerted SN2 or a stepwise SN1 mechanism. While theoretical investigations have provided estimates for the intrinsic activation energies associated with N-glycosidic bond cleavage reactions, experimental measurements to validate the theoretical studies remain elusive. Here we report experimental investigations for N-glycosidic bond cleavage of the protonated guanine nucleosides, [dGuo+H]+ and [Guo+H]+, using threshold collision-induced dissociation (TCID) techniques. Two major dissociation pathways involving N-glycosidic bond cleavage, resulting in production of protonated guanine or the elimination of neutral guanine are observed in competition for both [dGuo+H]+ and [Guo+H]+. The detailed mechanistic pathways for the N-glycosidic bond cleavage reactions observed are mapped via electronic structure calculations. Excellent agreement between the measured and B3LYP calculated activation energies and reaction enthalpies for N-glycosidic bond cleavage of [dGuo+H]+ and [Guo+H]+ in the gas phase is found indicating that these dissociation pathways involve stepwise E1 mechanisms in analogy to the SN1 mechanisms that occur in the condensed phase. In contrast, MP2 is found to significantly overestimate the activation energies and slightly overestimate the reaction enthalpies. The 2′-hydroxyl substituent is found to stabilize the N-glycosidic bond such that [Guo+H]+ requires ∼25 kJ mol−1 more than [dGuo+H]+ to activate the glycosidic bond.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...