Effects of solvent and supersaturation on crystal morphology of cefaclor dihydrate: a combined experimental and computer simulation study†
Abstract
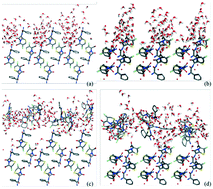
The modified attachment energy model was employed to predict cefaclor dihydrate morphology. Meanwhile, the mechanism and the effect of solvent and supersaturation on the crystal morphology were also proposed. A molecular dynamics simulation was applied to investigate the interactions of cefaclor dihydrate crystal faces with the pure solvent model and the solution model. The mechanism of solvent effects on the different faces was elaborated by discussing the surface structure and the adsorption of the crystal, while the effect of supersaturation was considered from the aspect of molecular recognition. The radial distribution function analysis was introduced to explore the adsorption behaviors of solvent and solute molecules. From the mean square displacement of solvent and solute molecules, the growth shape was affected by the solvent and solute diffusion capacity. The results suggested that the morphology evolution is due to the subtle competition of the molecular adsorptions between the solute and solvent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...