Visible light-driven water oxidation with a subporphyrin sensitizer and a water oxidation catalyst†
Abstract
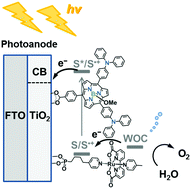
A new subporphyrin was synthesized for use as a molecular sensitizer in electrochemical and dye-sensitized photoelectrochemical water oxidation. A photoelectrochemical cell with a TiO2 electrode modified with the sensitizer and a molecular water oxidation catalyst generated higher photocurrent than reference cells that have electrodes modified with either the photosensitizer or the catalyst under visible light (λ > 500 nm) illumination. Oxygen evolution was confirmed after photolysis by GC and GC-MS analyses using isotope-labeling experiments. The large molar extinction coefficients of the ring-contracted porphyrin in the visible region enabled kinetic analysis by time-resolved transient absorption spectroscopy, which also supported the photocatalytic activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...