Enantioselective rhodium/ruthenium photoredox catalysis en route to chiral 1,2-aminoalcohols†
Abstract
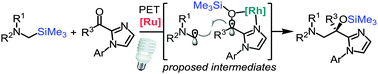
A rhodium-based chiral Lewis acid catalyst combined with [Ru(bpy)3](PF6)2 as a photoredox sensitizer allows for the visible-light-activated redox coupling of α-silylamines with 2-acyl imidazoles to afford, after desilylation, 1,2-amino-alcohols in yields of 69–88% and with high enantioselectivity (54–99% ee). The reaction is proposed to proceed via an electron exchange between the α-silylamine (electron donor) and the rhodium-chelated 2-acyl imidazole (electron acceptor), followed by a stereocontrolled radical–radical reaction. Substrate scope and control experiments reveal that the trimethylsilyl group plays a crucial role in this reductive umpolung of the carbonyl group.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...