Interfacial nano-biosensing in microfluidic droplets for high-sensitivity detection of low-solubility molecules†
Abstract
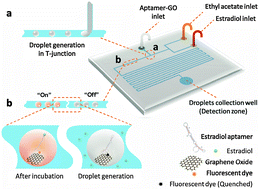
Taking advantage of the properties of the high surface-area-to-volume ratio of microfluidic droplets, we developed an innovative interfacial nanosensing strategy based on aptamer-functionalized graphene oxide nanosensors in microfluidic droplets for the high-sensitivity one-step detection of 17β-estradiol and other low-solubility molecules, with the detection sensitivity improved by about 3 orders of magnitude compared to conventional systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...