Rapid acquisition of high-affinity DNA aptamer motifs recognizing microbial cell surfaces using polymer-enhanced capillary transient isotachophoresis†
Abstract
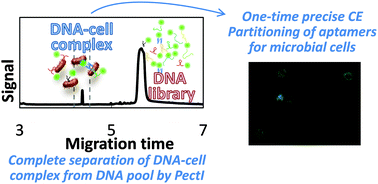
We present a polymer-enhanced capillary transient isotachophoresis (PectI) selection methodology for acquisition of high-affinity (kinetically inert) DNA aptamers capable of recognizing distinct microbial cell surfaces, which requires only a single electrophoretic separation between particles (free cells and cells bound with aptamers) and molecules (unbound or dissociated DNA) in free solution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...