Synthesis of ROS scavenging microspheres from a dopamine containing poly(β-amino ester) for applications for neurodegenerative disorders†
Abstract
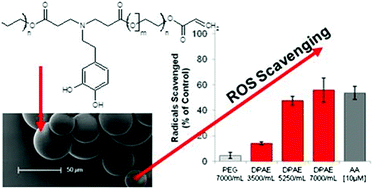
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disease characterized by a substantial decrease of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. The neurological deterioration during PD can be, in part, attributed to elevated levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Radical scavengers have previously been shown to protect dopaminergic cells from toxic effects in vitro. Hence, new approaches need to be investigated to improve the administration of antioxidants in order to provide neuroprotection. Polymers exhibiting catechol structures offer one such approach due to their interesting physicochemical properties. In the present study a photocrosslinkable dopamine-containing poly(β-amino ester) (DPAE) was synthesized from poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) and dopamine hydrochloride using Michael type addition. A water-in-oil emulsion technique was used to photo-crosslink the polymer into spherical microparticles. DPAE microspheres featured excellent scavenging properties towards 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) radicals in a dose dependent manner and could even reduce the dissolved oxygen content of physiological solution. Furthermore, the concentrations required for radical scavenging were shown to be non-toxic towards dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells as well as primary astrocytes and primary embryonic rat ventral midbrain cultures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...