Routine determination of inorganic arsenic speciation in precipitates from acid mine drainage using orthophosphoric acid extraction followed by HPLC-ICP-MS†
Abstract
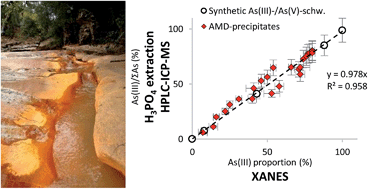
A simple chemical extraction method is proposed for the routine determination of the proportions of As(III) and As(V) species in iron-rich precipitates originating from acid mine drainage (AMD). The procedure consists of orthophosphoric acid (1 M) extraction and subsequent analysis of As(III) and As(V) concentrations in the extract by HPLC-ICP-MS. The proposed method was validated on a series of synthetic As(III)/As(V)-schwertmannite samples and of AMD samples exhibiting various mineralogical compositions, total As concentration, As/Fe and As(III)/ΣAs ratios as determined by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), total digestion-ICP-MS and synchrotron-based X-ray Absorption Near Edge Structure spectroscopy (XANES), respectively. High arsenic extraction efficiency (99 ± 10% of total As) was achieved with orthophosphoric acid since As-bearing iron phases that form in AMD are poorly crystalline. As(III) and As(V) proportions determined using the chemical extraction method followed by HPLC-ICP-MS analysis well matched the arsenic redox data obtained from the As K-edge XANES spectra analysis, showing the possibility to routinely measure the As oxidation state in AMD precipitates using this new simple extraction method.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...