1H NMR as a release methodology for the analysis of phospholipids and other constituents in infant nutrition†
Abstract
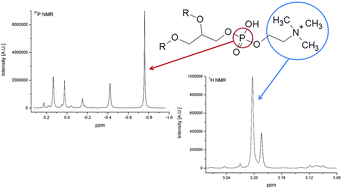
An 1H NMR method was developed to control five phospholipid (PL) species, namely, phosphatidylcholine (PC), sphingomyelin (SPH), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidylinositol (PI) in infant nutrition. The 1H NMR method for the PC, SPH, PE and PI species was validated according to the good laboratory practice (GLP) principles. The limits of detection and limits of quantification were below 0.0290 mg and 0.059 mg (300 mg sample weight), respectively. The coefficients of variation did not exceed 3.0% for PC and SPH and 10% for PE and PI and linearity was shown between 150 and 450 mg sample weight. The recovery was between 97.7% and 107.2% on average. Lorenz deconvolution, partial least squares (PLS) regression and independent component analysis (ICA) were successfully applied to extract PL signals in the case of spectral overlap. The root mean square error of prediction and the limit of quantification of the PLS model for PS were 0.026% w/w and 0.10% w/w, respectively. Other components (triacylglycerols, fatty acid, sterols, organic acids, carbohydrates, and inorganic cations) were additionally detected. NMR is suitable for the simultaneous qualitative measurement of major organic and inorganic compounds and is fit-for-purpose for quantitative determination of PLs in infant nutrition.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...