Whole blood analysis using microfluidic plasma separation and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay devices
Abstract
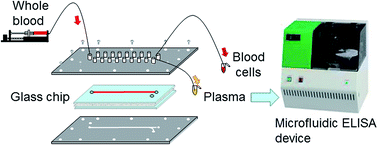
In this study, a microfluidic plasma-separation device that realizes the whole blood analysis of C-reactive protein (CRP) using one drop of blood is developed. A small, fast, and easy-to-operate blood-testing device is desirable for point-of-care testing, home medical care, and medical cost reduction. Recently, significant advances have been made in analytical instrumentation, and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of a 1 μL plasma sample has previously been realized. Moreover, recent developments in microfluidics have led to the miniaturization of analytical instruments. However, analytical centrifuges that are conventionally used for the separation of plasma and blood cells are very large and cumbersome to combine with microfluidic devices. Therefore, we propose a plasma-separation device combining microfluidics and membrane filtering. Herein, the proposed plasma-separation device is applied to whole blood analysis using one drop of blood. Specifically, the device is designed and fabricated to realize high plasma-separation efficiency via the evaluation of fluidic resistance of a porous membrane. Then, the quality of the plasma separated using the device is evaluated and compared with that of the plasma separated using a conventional centrifuge. Our results reveal that the microfluidic plasma-separation device can efficiently provide a sample for the ELISA of CRP using one drop (50 μL) of whole blood. The total analysis time including plasma separation and ELISA is approximately 25 min.
- This article is part of the themed collection: In memory of Craig Lunte

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...