Simultaneous quantification of bisphenol A, alkylphenols and alkylphenol ethoxylates in indoor dust by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and a comparison between two sampling techniques†
Abstract
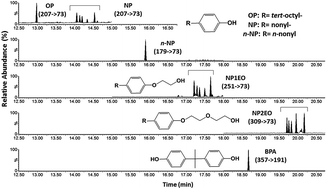
A method based on gas chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS) was chosen over liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) for the simultaneous measurement of bisphenol A (BPA), 4-tert-octylphenol (OP), 4-n-nonylphenol (n-NP), 4-nonylphenol (NP), 4-nonylphenol monoethoxylate (NP1EO), and 4-nonylphenol diethoxylate (NP2EO) in indoor dust. The GC-MS/MS-based method demonstrated high sensitivity, with method detection limits (MDLs) ranging from 0.06 to 0.16 μg g−1. Two types of dust samples were collected using two methods: fresh dust (FD) sampling and household vacuum (HD) sampling. Comparisons of FD and HD samples collected from a subset of 44 homes were based on Spearman rank test. Significant correlations were found for the majority of the target analytes (i.e., BPA, NP, NP1EO and NP2EO), suggesting that household vacuum sampling could be used as an alternative to the expensive fresh dust sampling. Target compounds were then analyzed in 260 HD samples collected from randomly selected urban Canadian single family dwellings as part of the Canadian House Dust Study (CHDS). All target compounds were detected with high frequency (>99%); the most predominant compounds were NP, NP1EO, NP2EO and BPA, with median concentrations (range in parenthesis) of 6.84 (1.0–84.2) μg g−1, 2.13 (0.39–20.4) μg g−1, 2.84 (<0.16–28.1) μg g−1, and 1.78 (0.25–24.0) μg g−1, respectively. High detection frequency and widely scattered concentrations of target analytes in this set of 260 HD samples indicate that indoor house dust may constitute one of the major routes for human exposure to these compounds.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...