A novel aptamer–quantum dot fluorescence probe for specific detection of antibiotic residues in milk
Abstract
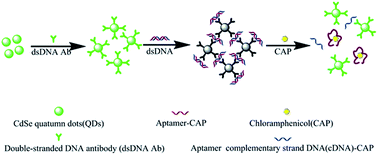
Herein, a facile, signal-on and homogenous fluorescence assay using novel aptamer-dsDNA antibody–quantum dot probes was designed for detecting antibiotic residues. In this assay, the fluorescent probes were fabricated by using a double-stranded DNA antibody (dsDNA Ab) covalently bonded on the surface of CdSe quantum dots. The antibody can bind double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) specifically. When dsDNA was added, the fluorescence could be efficiently quenched because the probes came into contact with each other with dsDNA as the bridge. The dsDNA was formed between an aptamer towards chloromycetin (CAP) and its complementary strand DNA (cDNA). When CAP was added into the reaction system, the aptamer reacted with CAP preferentially and the dsDNA was unwinded to single strand DNA (ssDNA) which cannot be recognized by the dsDNA antibody. Thus the probes were separated and fluorescence was recovered. Based on the scheme, a signal-on fluorescence assay for detecting antibiotics in a homogenous aqueous phase was developed. Under the optimized conditions, the assay shows a good liner range from 0.05 ng mL−1 to 100 ng mL−1 and the limit of detection (LOD) is 0.002 ng mL−1. If the analyte is changed, the assay can also be employed only by changing the corresponding aptamer and its cDNA. What's more, the probes can be reused at least 10 times with the recovery above 90%. The fluorescence assay is facile and has promising application for detecting antibiotic contaminants in biological and environmental samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...