Voltammetric quantitation of acetaminophen in tablets using solid graphite electrodes
Abstract
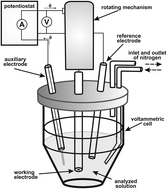
The aim of the study was to develop a voltammetric method for acetaminophen determination in aqueous solutions prepared from simple and complex pharmaceutical formulations using unmodified solid graphite electrodes. In search for optimized conditions four different voltammetry techniques were applied – cyclic voltammetry (CV), normal pulse voltammetry (NPV), differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) and square wave voltammetry (SqWV) with a potential sweep from 100 to 900 mV. The effect of other parameters was also verified e.g. the volume ratio between electrolyte and depolarizer, supporting electrolyte type (phosphate, ammonium-acetic, citric-phosphate buffers and glacial acetic acid) and pH. The distinct oxidation peak emerged in DPV in the presence of phosphate buffer pH 7.88 at 370 mV. The linear range between the potential peak current and the concentration of the standard solution of acetaminophen was established between 3 and 15 mg L−1. The limits of detection and quantification were equal to 0.3017 and 0.9144 mg L−1, respectively. The developed method is simple, reliable and sufficiently accurate and precise for quantitation of acetaminophen in simple and complex solid dosage forms (tablets).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...