Development of an electrochemical nanosensor for the determination of gallic acid in food
Abstract
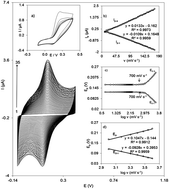
In the present work, a silver nanoparticle/delphinidin modified glassy carbon electrode (AgNP/Delph/GCE) was fabricated as a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for gallic acid (GA) determination. Cyclic voltammetry experiments indicated a higher sensitivity and better selectivity for gallic acid when using the AgNP/Delph/GCE as compared with the bare GCE surface, which were attributed to AgNPs and delphinidin, respectively. Moreover, the calculated surface electron transfer rate constant (ks), and the electron transfer coefficient (α) between the GCE and the electrodeposited delphinidin demonstrated that delphinidin is an excellent electron transfer mediator for the electrocatalytic process. The average catalytic rate constant (k′) of the overall process was also estimated to be 7.40 × 10−4 cm s−1 for the AgNP/Delph/GCE in the presence of 1.50 mmol L−1 of GA. Amperometry experiments were used to determine the limit of detection of the AgNP/Delph/GCE electrochemical sensor, which was 0.28 μmol L−1 of GA. Finally, two linear ranges were found, i.e. 0.60–8.68 μmol L−1 and 8.68–625.80 μmol L−1 for GA. The activity of the modified electrode was eventually investigated to assess the potential quantification of GA in real foods.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...