A rapid and novel method for predicting nicotine alkaloids in tobacco through electronic nose and partial least-squares regression analysis
Abstract
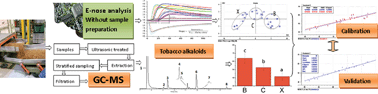
Alkaloid levels in tobacco are of great concern owing to nicotine addiction and associated diseases. A rapid method of analyzing tobacco alkaloids is required for legislatures and tobacco companies. This study aims to establish prediction models of tobacco alkaloids via responses of an electronic nose and partial least-squares regression (PLSR) for the rapid analysis of alkaloid levels in tobacco. Eight alkaloids (nicotine and myosmine) were detected by gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (GC-TriQ-MS). The characterization of alkaloids from different leaf positions (upper (B), middle (C) and lower (X)) was investigated and three signal features of electronic nose sensors were selected for better modeling. The results showed that the total alkaloid content significantly varied in the following order: B > C > X. The sensors' maximum intensity (INmax) and slope (K) were significantly related to the alkaloid levels. Prediction models for alkaloids were successfully established. The calibrated (R_cal = 0.99 and R_cal2 = 0.98) and validated (R_val = 0.97, R_val2 = 0.94) parameters of the nicotine prediction model were very satisfactory. After checking for validity, the established model for nicotine detection has a predictive capability of 96%. Moreover, the predictive effectiveness of models of other alkaloids (except nicotyrine) was also proved to be accurate. This study provided evidence that an electronic nose could be used as a testing tool to rapidly and quantitatively detect the content of nicotine alkaloids in tobacco. Further study is still needed to improve the precision and robustness of the alkaloid calibration models.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...