Reflection scanometry as a new detection technique in temperature-controlled ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid phase microextraction
Abstract
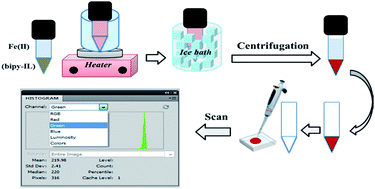
Coupling of temperature-controlled ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid phase microextraction (TCIL-DLPME) with reflection scanometry for quantitative determination of colored species in solution is introduced for the first time. To evaluate the performance and applicability of the methodology, the ferrous ion which forms a red complex with 2,2′-bipyridyl (bipy) was used as the model analyte. The ionic liquid (IL) 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate was used for extracting the complex by TCIL-DLPME after diluting the IL phase with dimethylformamide, which was injected into the detection chamber in a Plexiglas® sheet. It was scanned with a conventional flatbed-scanner. The color of the image was analyzed for its R (red), G (green), and B (blue) components using Adobe Photoshop software. Optimization of the parameters affecting the extraction process as well as the calibration curve was based on the G (green) color value as the analytical signal. Some essential parameters including the IL chemical structure, volume of IL, bipy concentration, pH, temperature, centrifugation time, and aqueous phase volume have been studied in detail. Under optimum experimental conditions the method was successfully applied for the determination of Fe(II) in iron supplement oral drop (IroVit) and boiler water samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...