Silver nanoparticle functionalized glass fibers for combined surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy (SERS)/surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization (SALDI) mass spectrometry via plasmonic/thermal hot spots†
Abstract
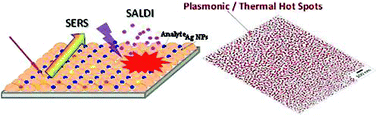
We presented the fabrication of a silver nanoparticle (Ag NP) functionalized glass fiber (Ag-GF) substrate for combined surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy (SERS)/surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization (SALDI) mass spectrometry. Ag NPs were immobilized onto the surface of glass fibers through a simple sputter deposition process. The SERS and SALDI activities strongly depended on the nanostructures of the deposited Ag NPs on the GFs. The closely-packed Ag NPs with a size of 20–50 nm and an inter-particle nanoscale gap of less than 10 nm were effective for the simultaneously enhanced SERS/SALDI substrate via plasmonic/thermal “hot spots”, while the interconnected continuous Ag film reduced both the SERS/SALDI activities. The SERS enhanced factor (EFSERS) and SALDI enhanced factor (EFSALDI) were newly proposed. Finally, the concentration-dependent signal intensities of SERS and SALD-MS of sulfur compounds using an identical Ag NP-GF substrate were examined, and the linear dependence relationship in the log–log plot was demonstrated for the combined quantitative SERS/SALDI-MS analysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...