A peptide with a cysteine terminus: probe for label-free fluorescent detection of thrombin activity†
Abstract
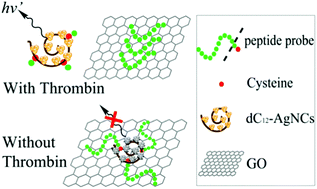
Thrombin has been implicated in atherosclerotic disease development. However, thrombin activity detection is currently limited because of the lack of convenient fluorescent probes. We developed a label-free fluorescent method to assay thrombin activity on the basis of a designed peptide probe with a thrombin-cleavable peptide sequence and a cysteine terminus. The peptide probe can be conjugated to DNA-templated silver nanoclusters (DNA-AgNCs) through Ag–S bonding; as a result, the fluorescence of DNA-AgNCs was enhanced. As the DNA-AgNCs–peptide conjugate was adsorbed to graphene oxide (GO), the enhanced fluorescence of DNA-AgNCs was quenched. Once the peptide probe was cleaved by thrombin, the resulting release of the DNA-AgNCs from the surface of GO restored the enhanced fluorescence. Thrombin can be determined with a linear range of 0.0–50.0 nM with a detection limit of 1 nM. The thrombin-sensitive probe with a cysteine terminus may be developed into probes to detect other proteases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...