Development of an integrated microfluidic solid-phase extraction and electrophoresis device†
Abstract
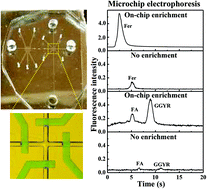
This study focuses on the design and fabrication of a microfluidic platform that integrates solid-phase extraction (SPE) and microchip electrophoresis (μCE) on a single device. The integrated chip is a multi-layer structure consisting of polydimethylsiloxane valves with a peristaltic pump, and a porous polymer monolith in a thermoplastic layer. The valves and pump are fabricated using soft lithography to enable pressure-based fluid actuation. A porous polymer monolith column is synthesized in the SPE unit using UV photopolymerization of a mixture consisting of monomer, cross-linker, photoinitiator, and porogens. The hydrophobic, porous structure of the monolith allows protein retention with good through flow. The functionality of the integrated device in terms of pressure-controlled flow, protein retention and elution, on-chip enrichment, and separation is evaluated using ferritin (Fer). Fluorescently labeled Fer is enriched ∼80-fold on a reversed-phase monolith from an initial concentration of 100 nM. A five-valve peristaltic pump produces higher flow rates and a narrower Fer elution peak than a three-valve pump operated under similar conditions. Moreover, the preconcentration capability of the SPE unit is demonstrated through μCE of enriched Fer and two model peptides in the integrated system. FA, GGYR, and Fer are concentrated 4-, 12-, and 50-fold, respectively. The loading capacity of the polymer monolith is 56 fmol (25 ng) for Fer. This device lays the foundation for integrated systems that can be used to analyze various disease biomarkers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...