C10H4O2S2/graphene composite as a cathode material for sodium-ion batteries†
Abstract
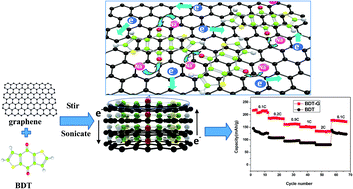
Organic electroactive materials are promising candidates for next generation sodium ion batteries (SIBs) due to their low cost, sustainability and environmental benignity. It is of great interest to develop organic compounds with multifunctional groups to be used as electrode materials for SIBs owing to their light weight, multi-electron reactions, redox stability and structural diversity. The organic compound 4,8-dihydrobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b′] dithiophene-4,8-dione (BDT) was prepared by a facile solution method, and its graphene composite (BDT–G) was synthesized by a simple dispersion–deposition process. BDT–G as a cathode material demonstrated much enhanced electrochemical performance, including higher reversible capacity (217 mA h g−1vs. 145 mA h g−1), better cycling performance (∼175 mA h g−1vs. ∼100 mA h g−1 after 70 cycles at 0.2C), and higher rate capabilities (1.7 times better than BDT at 2C) compared with BDT. It is revealed that these improved electrochemical properties should be mainly attributed to the excellent electronic conductivity and ionic transport efficiency promoted by graphene. Furthermore, the fast electrode reaction of BDT with the help of unlimited electron transport via the two-dimensional graphene network results in enhanced usage of materials, and BDT in the composite with graphene could be inhibited from dissolution in the organic electrolyte.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...