Electrochemical properties of silver nanoparticle-supported reduced graphene oxide in nitric oxide oxidation and detection†
Abstract
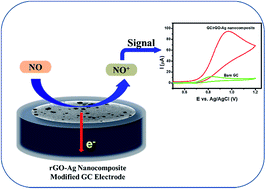
This article reports the effect of ascorbic acid in the formation of a reduced graphene oxide–silver (rGO–Ag) nanocomposite and its influence on the electrochemical oxidation of nitric oxide (NO). The formation of the rGO–Ag nanocomposite was confirmed using UV-visible absorption spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses. Crystalline and spherical Ag nanoparticles (NPs) with an average particle size of 2 nm were found in the rGO–Ag nanocomposite with the assistance of 5.0 M ascorbic acid. The electrochemical properties of the rGO–Ag nanocomposite-modified glassy carbon (GC) electrode were investigated for the oxidation of NO. The rGO–Ag (5.0 M) nanocomposite-modified electrode displayed a higher catalytic current response compared to other controlled modified electrodes in cyclic voltammetry toward the oxidation of NO in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 2.5). The electroanalytical application of the nanocomposite was performed using an amperometry technique, and the limit of detection (LOD) was found to be 2.84 μM for the in situ detection of NO. The present nanocomposite was stable, sensitive, and selective in the presence of the common physiological interferents such as ascorbic acid, uric acid, dopamine, glucose, urea, and NaCl.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...