Mechanically strong fully biobased anisotropic cellulose aerogels†
Abstract
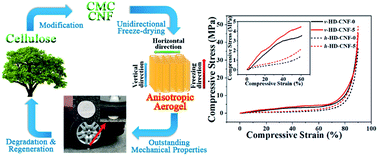
Fully biobased chemically crosslinked anisotropic carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)/cellulose nanofibril (CNF) aerogels were prepared using an environmentally friendly directional freeze-drying method. The resulting cellulose aerogels were characterized using various techniques. It was found that the CMC/CNF aerogel exhibited a honeycomb structure, and thus possessed anisotropic properties. Moreover, the fully biobased crosslinked organic aerogel possessed excellent mechanical properties based on both compression and three-point bending tests. For instance, it exhibited a remarkable compressive modulus (up to 10 MPa) along the vertical direction (parallel to the freezing direction) as well as a high flexural modulus (up to 54 MPa) perpendicular to the freezing direction. The effects of different aerogel densities and CNF contents on the mechanical properties of CMC/CNF aerogels have been studied. With increasing aerogel density or CNF content, the modulus and strength of the CMC/CNF aerogel increased in both compression and three-point bending tests. In addition, these cellulose aerogels also exhibited relatively low thermal conductivities (<54 mW m−1 K−1). Considering their excellent mechanical properties, very low densities, and the “green” synthesis process, these CMC/CNF aerogels hold great promise for potential industrial applications such as green thermal insulation building materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...