Transport properties of microemulsions with ionic liquid apolar domains as a function of ionic liquid content†
Abstract
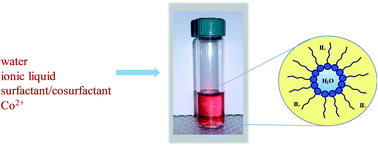
The specific conductivity, dynamic viscosity and apparent diffusion coefficient of each of four aqueous ionic liquid microemulsions (IL-MEs) were measured as a function of ionic liquid (IL) content. The investigated systems were composed of water, hydrophobic ILs (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate or bis(trifluoromethanesulphonyl)imide) and the nonionic surfactant Triton X-100 or its mixture with cosurfactant (butanol). Measurements were conducted across the whole IL content range, and results are discussed in terms of the anion type and the influence of cosurfactant. The comparative approach revealed that IL-MEs exhibit higher conductivity than pure ILs, that addition of cosurfactant further increases the conductivity of the system, and that the increase depends on the anion structure. Furthermore, addition of cosurfactant causes a serious decrease in viscosity which is beneficial since high viscosity is one of the factors limiting the broader use of ILs. The apparent diffusion coefficients, measured with cyclic voltammetry, exhibited good consistency with values obtained by other techniques and allowed closer insight into the properties and structures of the studied systems. The conclusions were supported by UV-Vis as well as FTIR spectrophotometric measurements. The pronounced facilitation of transport properties is favorable to many applications such as synthesis or separation processes. This is the first work regarding the dependence of IL-based ME properties on IL content.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...