N-(7-Chloroquinolinyl-4-aminoalkyl)arylsulfonamides as antimalarial agents: rationale for the activity with reference to inhibition of hemozoin formation†
Abstract
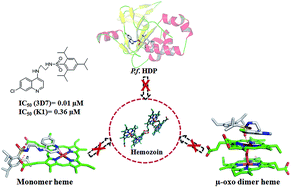
New N-(7-chloroquinolinyl-4-aminoalkyl)arylsulfonamides were synthesized and tested in vitro against P. falciparum 3D7 and K1 strains and hemozoin formation. Compounds 16 and 17 showed promising antimalarial activity (IC50 3D7: 0.05 and 0.01 μM; K1: 0.41 and 0.36 μM) and exceedingly well inhibited hemozoin formation (IC50, 3.23 and 2.40 μM). Considering hemozoin inhibition was due to the affinity of the compounds towards heme, its μ-oxo dimer and/or heme detoxification protein (HDP), they were used in docking experiments for probing intermolecular interactions with the compounds. The docked structures indicated that quinoline, 4-amino and sulfonamide moieties interacted with one or more key constituents of the targets. In heme and μ-oxo dimer, the key constituents for interactions were ferriprotoporphyrin and propionic acid side chains. In the case of HDP, the key constituents were His175 and Glu126, and rationalized the antimalarial activity and functional use of the sulfonamide moiety. Thus, these compounds opened an avenue for exploration of hemozoin inhibition in malaria chemotherapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...