pH-Triggered copolymer micelles as drug nanocarriers for intracellular delivery†
Abstract
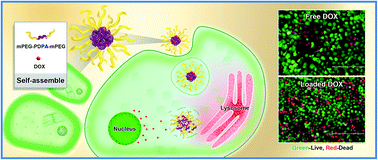
One growing issue is how to use the weakly acidic conditions in endosomes/lysosomes for designing highly pH-sensitive drug carriers to deliver chemotherapeutic drugs accurately. In this paper, pH-sensitive amphiphilic triblock copolymers PEG8-PDPAn-PEG8 (n = 30, 50 and 100) were synthesized. Micelles composed of the copolymers were found to enter into lysosomes using a lysosome tracker method. The pH-sensitivity makes the micelles stable at pH 7.4 but swell and become looser at pH 6.0 due to protonation. Then, doxorubicin (DOX) was efficiently encapsulated in the hydrophobic cores of the micelles and released continuously in a weakly acidic environment. Cell toxicity assays were carried out using 2 human cell lines (HEK293 and Huh7) and showed good cyto-compatibility. In vitro cell viability tests proved that the DOX-loaded micelles could be more efficiently taken up by Huh7 tumor cells than free DOX, as well as actively trigger intracellular DOX release. Furthermore, in addition to small molecules (DOX), the copolymer micelles could also deliver macromolecules (such as transferrin, which could not enter into cells by itself) into lysosomes/endosomes. These nontoxic and multifunctional micelles can serve as a promising treatment candidate for efficient intracellular drug delivery and real-time monitoring.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...