Towards the development of eco-friendly disposable polymers: ZnO-initiated thermal and hydrolytic degradation in poly(l-lactide)/ZnO nanocomposites†
Abstract
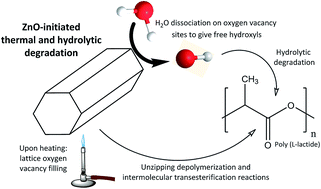
In this work poly(L-lactide)/ZnO nanocomposites with homogeneously distributed nanoparticles have been fabricated by a solvent-precipitation method. The obtained nanocomposites have been submitted to thermal and hydrolytic degradation processes in order to elucidate the catalytic effect of ZnO nanoparticles. The resulting degradation products from the thermally-initiated catalysis have been identified by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). It has been found that the presence of ZnO gives rise to a 65-fold increase in the formation of CO2 in comparison to acetaldehyde. FTIR results of hydrolytically degraded nanocomposites show an increased amount of carboxylic acid groups as ZnO concentration increases, while the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching band splitting denoted larger crystalline regions as degradation proceeds. The obtained results are explained from the viewpoint of lattice oxygen vacancies in ZnO. Upon thermodegradation nanoparticles initiate unzipping depolymerization/intermolecular transesterification reactions in PLLA, while during hydrolytic degradation H2O is dissociated on oxygen vacancy sites, giving hydroxyl groups that initiate the hydrolysis of ester bonds, and thus reducing PLLA to soluble monomers. The obtained findings are expected to allow the development of eco-friendly disposable polymeric waste by opening new possibilities in the use of naturally-available materials as efficient catalysts for feedstock recycling of biopolymers by common chemical processes.
O stretching band splitting denoted larger crystalline regions as degradation proceeds. The obtained results are explained from the viewpoint of lattice oxygen vacancies in ZnO. Upon thermodegradation nanoparticles initiate unzipping depolymerization/intermolecular transesterification reactions in PLLA, while during hydrolytic degradation H2O is dissociated on oxygen vacancy sites, giving hydroxyl groups that initiate the hydrolysis of ester bonds, and thus reducing PLLA to soluble monomers. The obtained findings are expected to allow the development of eco-friendly disposable polymeric waste by opening new possibilities in the use of naturally-available materials as efficient catalysts for feedstock recycling of biopolymers by common chemical processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...