Identification of the binding roles of terminal and internal glycan epitopes using enzymatically synthesized N-glycans containing tandem epitopes†
Abstract
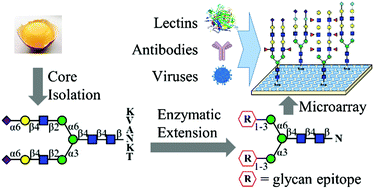
Glycans play diverse roles in a wide range of biological processes. Research on glycan-binding events is essential for learning their biological and pathological functions. However, the functions of terminal and internal glycan epitopes exhibited during binding with glycan-binding proteins (GBPs) and/or viruses need to be further identified. Therefore, a focused library of 36 biantennary asparagine (Asn)-linked glycans with some presenting tandem glycan epitopes was synthesized via a combined Core Isolation/Enzymatic Extension (CIEE) and one-pot multienzyme (OPME) synthetic strategy. These N-glycans include those containing a terminal sialyl N-acetyllactosamine (LacNAc), sialyl Lewis x (sLex) and Siaα2–8-Siaα2–3/6-R structures with N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) or N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc) sialic acid form, LacNAc, Lewis x (Lex), α-Gal, and Galα1–3-Lex; and tandem epitopes including α-Gal, Lex, Galα1–3-Lex, LacNAc, and sialyl LacNAc, presented with an internal sialyl LacNAc or 1–2 repeats of an internal LacNAc or Lex component. They were synthesized in milligram-scale, purified to over 98% purity, and used to prepare a glycan microarray. Binding studies using selected plant lectins, antibodies, and viruses demonstrated, for the first time, that when interpreting the binding between glycans and GBPs/viruses, not only the structure of the terminal glycan epitopes, but also the internal epitopes and/or modifications of terminal epitopes needs to be taken into account.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...