A cobalt oxyhydroxide nanoflake-based nanoprobe for the sensitive fluorescence detection of T4 polynucleotide kinase activity and inhibition†
Abstract
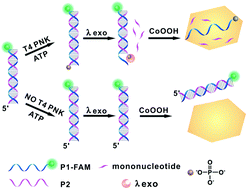
Phosphorylation of nucleic acids with 5′-OH termini catalyzed by polynucleotide kinase (PNK) is an inevitable process and has been implicated in many important cellular events. Here, we found for the first time that there was a significant difference in the adsorbent ability of cobalt oxyhydroxide (CoOOH) nanoflakes between single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), which resulted in the fluorescent dye-labeled dsDNA still retaining strong fluorescence emission, while the fluorescence signal of ssDNA was significantly quenched by CoOOH nanoflakes. Based on this discovery, we developed a CoOOH nanoflake-based nanoprobe for the fluorescence sensing of T4 PNK activity and its inhibition by combining it with λ exonuclease cleavage reaction. In the presence of T4 PNK, dye-labeled dsDNA was phosphorylated and then cleaved by λ exonuclease to generate ssDNA, which could adsorb on the CoOOH nanoflakes and whose fluorescence was quenched by CoOOH nanoflakes. Due to the high quenching property of CoOOH nanoflakes as an efficient energy acceptor, a sensitive and selective sensing approach with satisfactory performance for T4 PNK sensing in a complex biological matrix has been successfully constructed and applied to the screening of inhibitors. The developed approach may potentially provide a new platform for further research, clinical diagnosis, and drug discovery of nucleotide kinase related diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...