Water-soluble metal nanoparticles stabilized by plant polyphenols for improving the catalytic properties in oxidation of alcohols†
Abstract
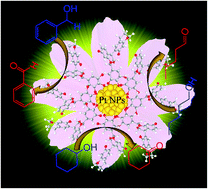
Plant polyphenols extracted from plants are one of the most abundant biomasses in nature, which are typical water soluble natural polymers. Herein, we reported a facile approach for the synthesis of platinum nanoparticle (PtNP) aqueous colloid by utilizing black wattle tannin (BWT, a typical plant polyphenol) as amphiphilic stabilizer. The phenolic hydroxyls of BWT provide the PtNPs with enough hydrophilicity, and their reduction ability could protect the PtNPs from deactivation caused by oxygen atmosphere. Additionally, the hydrophilic nature of BWT could efficiently promote the oxidation of alcohols in water, meanwhile, the hydrophobic and rigid backbones of plant polyphenols are able to suppress the PtNPs from aggregating, thus ensuring the high dispersion of the PtNPs during reactions. Under mild aerobic conditions, the as-prepared BWT-Pt colloid catalyst exhibited high activity in a series of biphasic oxidation of aromatic alcohols and aliphatic alcohols. As for the cycling stability, the BWT-Pt catalyst showed no obvious decrease during the 7 cycles, revealing superior cycling stability as compared with the counterparts using PVP or PEG as the stabilizer.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...