Self-assembly of subwavelength nanostructures with symmetry breaking in solution†
Abstract
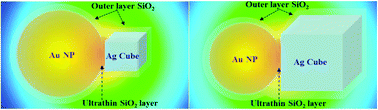
Nanostructures with symmetry breaking can allow the coupling between dark and bright plasmon modes to induce strong Fano resonance. However, it is still a daunting challenge to prepare bottom-up self-assembled subwavelength asymmetric nanostructures with appropriate gaps between the nanostructures especially below 5 nm in solution. Here we present a viable self-assembly method to prepare symmetry-breaking nanostructures consisting of Ag nanocubes and Au nanospheres both with tunable size (90–250 nm for Au nanospheres; 100–160 nm for Ag nanocubes) and meanwhile control the nanogaps through ultrathin silica shells of 1–5 nm thickness. The Raman tag of 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (MBA) assists the self-assembly process and endows the subwavelength asymmetric nanostructures with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) activity. Moreover, thick silica shells (above 50 nm thickness) can be coated on the self-assembled nanostructures in situ to stabilize the whole nanostructures, paving the way toward bioapplications. Single particle scattering spectroscopy with a 360° polarization resolution is performed on individual Ag nanocube and Au nanosphere dimers, correlated with high-resolution TEM characterization. The asymmetric dimers exhibit strong configuration and polarization dependence Fano resonance properties. Overall, the solution-based self-assembly method reported here is opening up new opportunities to prepare diverse multicomponent nanomaterials with optimal performance.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...