Bio-inspired magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on Pickering emulsions for selective protein recognition
Abstract
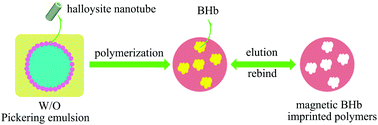
Novel magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (MMIPs) based on halloysite nanotube stabilized Pickering emulsion polymerization were successfully prepared using a facile approach for the high recognition and separation of proteins in aqueous solutions. The MMIPs were synthesized based on the self-polymerization of dopamine in weak alkaline solution in the presence of template protein. During the self-polymerization of dopamine in the water phase, the template proteins were embedded in polydopamine (PDA), and after the removal of the embedded template proteins, magnetic bovine hemoglobin (BHb) imprinted PDA@MHNTs (MHNTs, magnetic halloysite nanotubes) with complementary cavities were eventually obtained. The resulting samples were analyzed by Fourier transmission infrared (FT-IR) spectrometry, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The prepared MMIPs showed high adsorption capacity, good selectivity, rapid kinetic binding (70 min), stability (only 9% decrease after four cycles) and magnetic separability (3 min), which would endow the MMIPs with great potential in the field of protein separation and purification, biosensing, proteomics and biotherapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...