Core–shell magnetic Ag/AgCl@Fe2O3 photocatalysts with enhanced photoactivity for eliminating bisphenol A and microbial contamination
Abstract
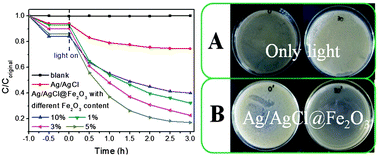
Core–shell magnetic Ag/AgCl@Fe2O3 photocatalysts were synthesized using a two-step method. The introduced Fe2O3 can be effectively dispersed on the surface of the Ag/AgCl. The Fe2O3 on the surface can act as a shell to prevent the inactivation of the inner Ag/AgCl by bisphenol A (BPA). The composites were investigated by XRD, SEM-EDS, XPS, UV-vis, VSM, and so on, which confirmed that the core–shell magnetic Ag/AgCl@Fe2O3 was successfully obtained. The EIS and PL results suggest that the composite has better electron–hole separation ability, which is beneficial for enhancing the photoactivity. The degradation of the BPA solution results show that the 5% Ag/AgCl@Fe2O3 has the highest photoactivity, the degradation rate of which is as high as about 13 times that of pure Ag/AgCl. Besides, the composites still have much better degradation ability than the pure Ag/AgCl in each cycle experiment. The photocatalytic antibacterial experiment showed that the composite could completely kill the pathogenic microorganism E. coli under visible light irradiation at 30 min. The results suggest that the core–shell magnetic Ag/AgCl@Fe2O3 can be used as an effective magnetic recyclable photocatalyst in eliminating the colorless pollutant bisphenol A and microbial contamination. Furthermore, a possible reaction mechanism was proposed based on the trapping experiments and the ESR results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...